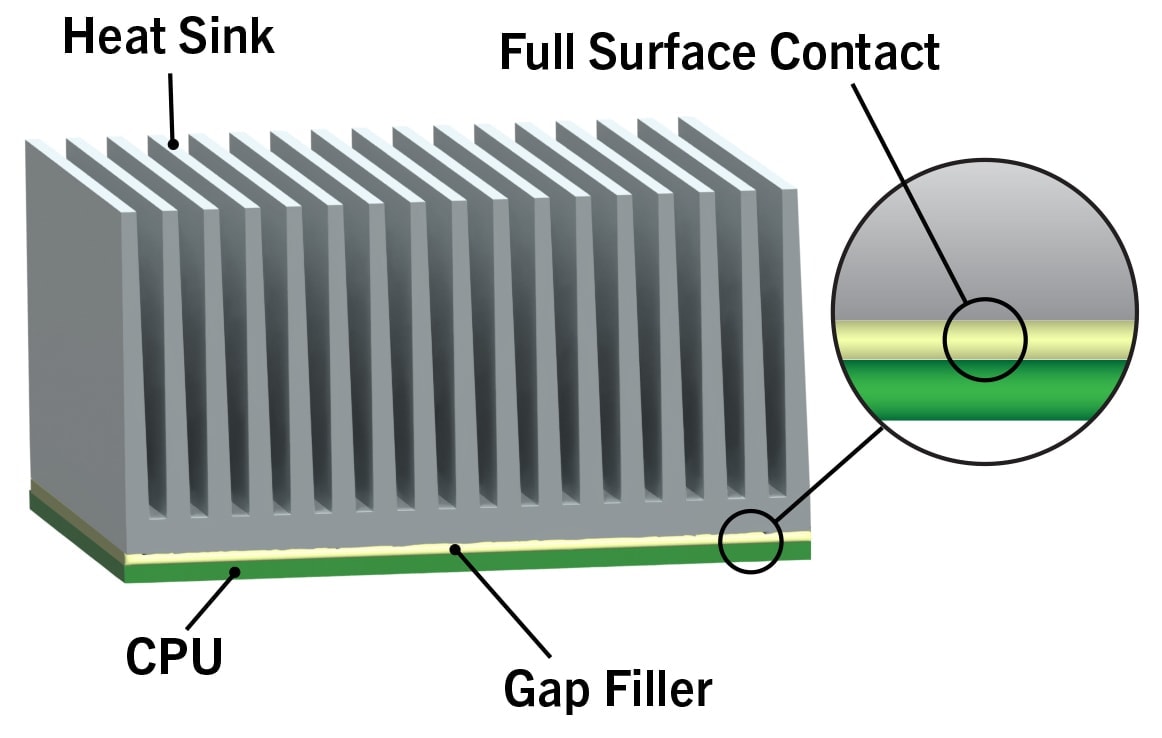
Proper thermal management of modern electronic circuitry is achieved using various materials like potting resins, adhesives, greases, and thermal gap fillers. Choosing the right product requires circuit designers to grasp the fundamental properties of thermal interface materials, so heat dissipation from the circuit is optimized. A thermal gap filler material is a popular choice since they polymerize and do not flow or dry out like grease yet can be easily removed, unlike an adhesive, for rework.
Features and Benefits of Gap Fillers
Several key features make gap fillers an exceptional heat dissipation material compared to other technologies like adhesives, greases, and thermal pads. Thermal gap fillers are 2-part silicone materials that cure upon the addition of heat to a putty-like consistency. These materials are applied as a soft paste onto the heat-generating component that connects to the heatsink, conducting heat out of the circuit and preventing overheating (please see our Tech Talk 1 video for application techniques). Unlike greases and thermal pads, which rely on line-of-sight application for complete coverage, gap fillers expand during cure, displacing air at the component/heatsink interface, making a tight-fitting connection, thus mitigating the risk of getting an insulating air pocket.
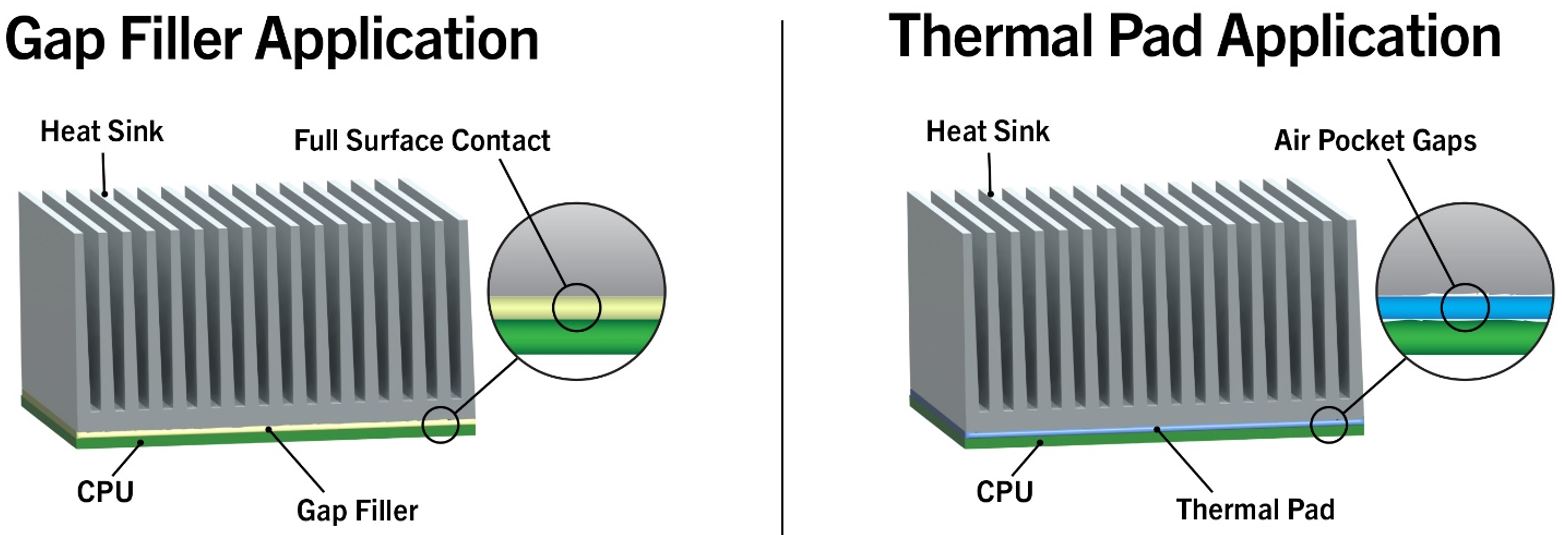
Thermal conductivity values for gap fillers range from 2 to 10 W/mk, substantially higher than most adhesives and greases. Another advantage is the low modulus of the cured material, making it an especially soft and conformal thermal interface material. Compression helps achieve very low bond lines, reducing thermal resistance, in line with other high performance thermal interface materials like thermal pads.
Industry Uses for Thermal Interface Materials
Gaps fillers are extremely soft materials that offer tacky adhesion, making them ideal for applications involving moving parts. They are a popular material for the thermal management of electronic control modules and mating batteries to cell packs within the automotive industry. In telecommunications, the constant flux of digital information means a lot of heat which demands the high thermal conductivity afforded by gap fillers over adhesives and greases.
